MAN Energy Solutions (MAN) has landed major compression and engine deals within the offshore gas and marine industries. Although the company has been supplying marine solutions for decades, the segment has evolved in recent years. Today, the business unit focuses on liquefied natural gas (LNG) supply, exhaust gas aftertreatment systems, hybrid marine propulsion systems, and optimized propulsion systems. The company is also investing heavily in hydrogen.
MAN has comprehensive expertise in the production, transport, storage, and conversion of green hydrogen. By 2030, it is investing more than US$540 million in its subsidiary, H-Tec Systems, with the intention of becoming a top-three global mass-producer of proton exchange membrane (PEM) electrolyzers. In February, MAN announced that H-Tec Systems will supply SailH2 with a 1-MW PEM electrolyzer for a green hydrogen project in Sevilla, Andalusia, Spain. H-Tec’s ME450 electrolyzer will be used in the Hub La Isla H2 project, a pilot hydrogen project that will examine a variety of different applications for green hydrogen, such as power-to-mobility, power-to-industry, and power-to-gas in the 4- to 20-MW range. During the initial project phase, SailH2 will combine 1 MW of hydrolysis power with 1.5-MW photovoltaic (PV) power, produced at a nearby PV plant. The hydrogen plant, using the PEM electrolyzer, will produce up to 136 tons (123 tonnes) of green hydrogen per year. H-Tec will deliver the electrolyzer in September 2024. After completion of Phase 1 in 2025, Phase 2 will explore the production and distribution of 680 tons (617 tonnes) of hydrogen for decarbonizing local industrial production processes.

Aside from its involvement in the production of green hydrogen, MAN is further supporting the hydrogen economy with its compression solutions. The company has more than 6500 compressors in operation, but it could be much more if the hydrogen economy takes off. Hydrogen must be pressurized and delivered as a compressed gas. Compressor stations for hydrogen pipelines will need units capable of safety handling hydrogen molecules that are magnitudes lighter and smaller than methane.
The following two deals illustrate the balance between proven solutions that maximize the quantity and efficiency of gas production, and the development of new technologies to support the burgeoning hydrogen economy.
Eleven MAN Compressors For Brazil FPSO
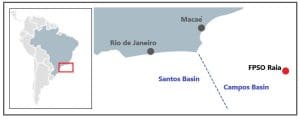
MAN will supply 11 RB-type compressor trains to Offshore Frontier Solutions Pte. Ltd., a MODEC Group company. The compressor trains will be installed on a floating production storage and offloading vessel (FPSO) for the Raia project in the Campos Basin, approximately 125 miles (200 km) off the coast of Rio de Janeiro.

Equinor, in partnership with Repsol Sinopec Brazil and Petrobras, will operate the FPSO, which is expected to produce up to 126,000 barrels of crude oil per day, and produce and export up to 565 MMscf/d (16 × 106 m3/d) of gas. The reservoir, located at a depth of around 9515 ft. (2900 m), is estimated to contain more than one billion barrels of oil equivalent.
The largest single order ever received at MAN Switzerland, the scope of supply for the FPSO’s gas lift, injection, and export application includes 11 electric motor-driven centrifugal compression trains, deployed as follows:
- two trains with type RB 28-6+3 compressors as overhead units
- two trains with type RB 45-4+5 compressors as low-pressure units
- five trains with type RB 28-5 compressors as medium- and high-pressure units
- two trains with type RB 28-8 compressors as gas injection units
The overhead and gas injection compressor units will be driven by fixed-speed electrical motors, whereas the high- and low-pressure units will be equipped with variable frequency drives (VFDs). Additionally, the two medium-pressure compressor units will feature a special switch control system, enabling operators to choose between fixed speed and VFD operation according to their requirements. The delivery of the compressor trains is scheduled for Q4 2024 and Q1 2025.
The MAN compression systems, once operational, will help maintain field pressure, thereby maximizing the quantity and efficiency of gas production. First production is expected in 2028.
The FPSO will apply MODEC’s new build, full double hull design, developed to accommodate larger topsides and larger storage capacity than conventional tankers. Taking advantage of this larger topside space, this FPSO will be the second fully electrified FPSO equipped with a combined cycle system for power generation, significantly reducing carbon emissions compared with conventional gas turbine-driven systems.
First Ever Hydrogen Test On A Marine Two-Stroke Engine
MAN’s licensee, Mitsui E&S Co. Ltd. (Mitsui), announced that it has successfully tested a 50-bore MAN B&W two-stroke engine up to 100% load while running on hydrogen, a first for the maritime industry. The engine was tested at Mitsui’s shipyard in Tamano, Japan, which was established in 1917.

In collaboration with MAN, Mitsui converted one of the four cylinders of a MAN B&W ME-GI (gas injection) engine to hydrogen operation. The hydrogen was supplied from a hydrogen gas-supply system that Mitsui developed in 2023.
Stable operation was achieved at various loads and operating conditions, including successful hydrogen combustion up to 100% load. Mitsui also confirmed greenhouse gas emissions reductions of up to 95%, with the remaining fraction originating from the pilot-fuel employed during testing.
“This is the world’s first successful hydrogen combustion test on a large, marine two-stroke engine,” Mitsui stated in a press release. “In achieving operation along with providing the hydrogen gas-supply system, we are now one step closer to developing a zero-emissions ship that uses hydrogen as fuel.”
“MAN B&W-branded engines are flexible by nature and designed for an easy retrofit at a later stage to different fuel types,” said Thomas S. Hansen, head of sales and promotion at MAN. “This is an encouraging milestone for hydrogen as a fuel. We will now take some time to evaluate the results and ensure that we are ready to take action if and when the market for hydrogen matures.”