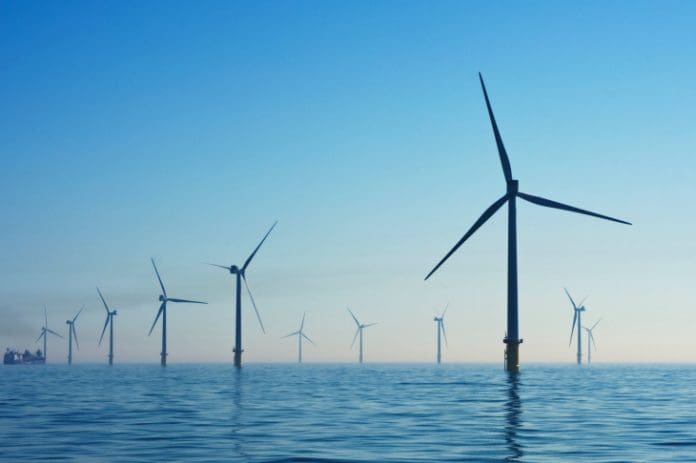
More and more countries are promoting the expansion of wind farms at sea to support the transformation toward a carbon-neutral energy production. However, if these offshore wind farms are set up close to each other, wind energy, and hence electricity yield, is reduced. A study by Germany research firm, Helmholtz-Zentrum Hereon, which has now been published in the Nature Scientific Reports journal, shows that the losses with increasing offshore wind energy production will be considerable and detectable due to a pattern of reduced wind speed around large-scale wind farms.
The expansion of wind energy in the German Bight and the Baltic Sea has accelerated enormously in recent years. The first systems went into operation in 2008. Today, wind turbines with an output of around 8000 MW rotate in German waters, which corresponds to around eight nuclear power plants. But space is limited. For this reason, wind farms are sometimes built very close to one another. A team led by Dr. Naveed Akhtar from Helmholtz-Zentrum Hereon has found that wind speeds at the downstream windfarm are significantly slowed down. This braking effect results in astonishingly large-scale, low-wind pattern noticeable in mean wind speeds. On average, they extend 22 to 25 mi. (35 to 40 km). And in certain weather conditions, they can even extend up to 62 mi. (100 km). The output of a neighboring wind farm can thus be reduced by 20% to 25%, which ultimately leads to economic consequences. If wind farms are planned close together, this wake effect needs to be considered in the future.
Combination Of Climate And Wind Farm Data
With their study, Naveed Akhtar, an expert in regional climate modeling, and his colleagues took a look into the future and assessed the wind characteristics for a medium-term target state of offshore expansion. They used the computer model COSMO-CLM, which is also used by weather services and is able to resolve weather situations regionally in detail (in this case for the entire North Sea) and combined it with the future wind farm characteristic (their area, and the number and size of the turbines). They used the wind farm planning for the North Sea from 2015 as a basis. This contains wind farms, some of which have not yet been built.
Braking Effect, Especially In Stable Weather Conditions
Naveed Akhtar used the COSMO model to calculate the wind speed over the North Sea for the period from 2008 to 2017, covering a range of different weather conditions. The results clearly show that we will face a large-scale pattern of reduced wind speed, which show largest extensions during stable weather conditions, typically the case in March and April. In stormy times, especially in November and December, the atmosphere is so mixed that the wind farm wake effects are relatively small. In order to verify the model data, the team compared the simulations with wind measurements from 2008 to 2017. They used measurements that were recorded on two research platforms in the North Sea and data from wind measurement flights that colleagues from the TU Braunschweig performed over existing wind farms. The comparison shows that the Hereon researchers are correctly simulating the wind wakes. What is special about the work is that for the first time a full ten-year period has been calculated for the entire North Sea. “Conventional flow models for analyzing wind farms have a very high spatial resolution, but only look at a wind field over a short period of time,” says Akhtar. “In addition, these cannot be used to determine how a wind farm changes the air flow over a large area.”
While the group has mainly dealt with the extent to which the wind farms influence each other in their current work, they intend to investigate in the near future what influence the reduced wind speeds have on life in the sea. Wind and waves mix the sea. This changes the salt and oxygen content of the water, its temperature, and the amount of nutrients in certain water depths. “We would now like to find out how the reduced mixing affects the marine ecosystem,” said Akhtar.