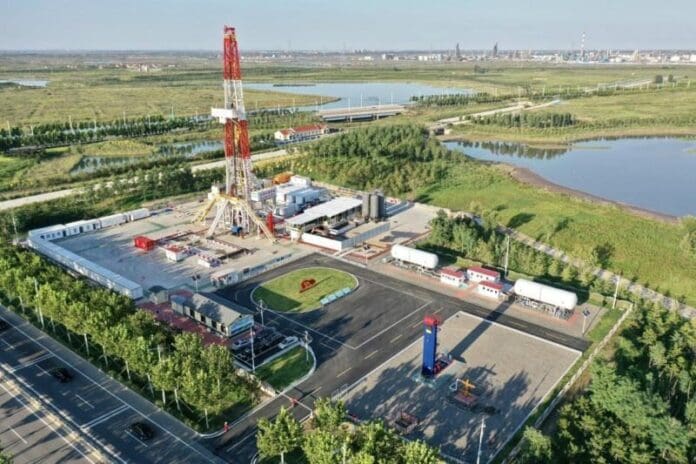
China Petroleum & Chemical Corporation Sinopec (Sinopec) has completed the construction of China’s first megaton carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) project, the Qilu-Shengli Oilfield CCUS. The plant will reduce carbon emissions by 1 million tons (907,185 tonnes) per year.
Construction began in July 2021 and consisted of two parts — Sinopec Qilu’s carbon dioxide capture and Shengli Oilfield’s carbon dioxide displacement and storage. The carbon dioxide captured by Sinopec Qilu will be transported to Shengli Oilfield for further displacement, storage, and well stimulation.
Sinopec Qilu constructed a liquid carbon dioxide recovery and utilization unit with a capacity of 1 million tons per year, which includes a compression unit, a refrigeration unit, a liquefaction refining unit, and supporting facilities to recover carbon dioxide from the tail gas of coal-to-hydrogen plants with a purification rate of more than 99%.
Meanwhile, Shengli Oilfield built 10 unattended gas injection stations in Zhenglizhuang Oilfield to inject carbon dioxide into the 73 wells nearby to increase crude oil fluidity and improve oil recovery while adopting a closed pipeline transportation of oil and gas to further enhance the carbon dioxide sequestration rate.
Looking Ahead
Sinopec has been planning to cap its carbon emissions at peak levels prior to a national timeline set by the government for 2030, both through its work to increase hydrogen output and the treatment and capture of carbon dioxide.
In the near term, Sinopec has aimed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 13.8 million tons (12.6 million tonnes) of carbon dioxide equivalent by 2023 from the 2018 level of 189.06 tons (171.52 million tonnes) and recycle methane emissions by 7.06 Bscf (200 × 106 m3).
To further advance CCUS development, Sinopec has announced plans to build a CCUS research and development center. The facility will focus technology developments, including the integration of CCUS with new energy, hydrogen energy, and biomass energy.
In addition, the company plans to build another megaton CCUS demonstration project in its affiliated Sinopec East China oil and gas fields and Sinopec Jiangsu Oilfield by 2025.